METABOLIC SYNDROME
What is Metabolic Syndrome?
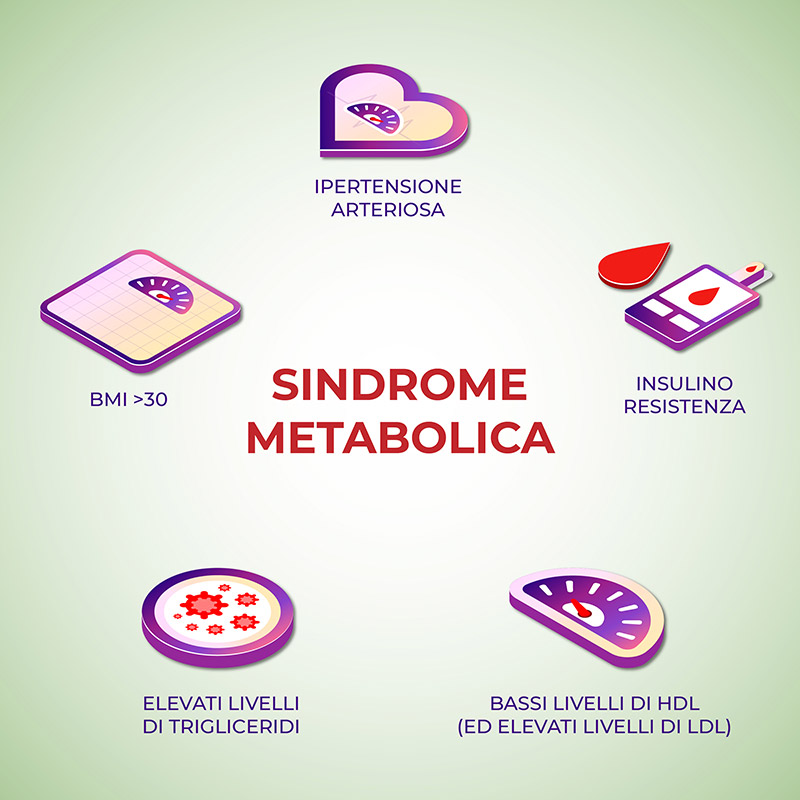
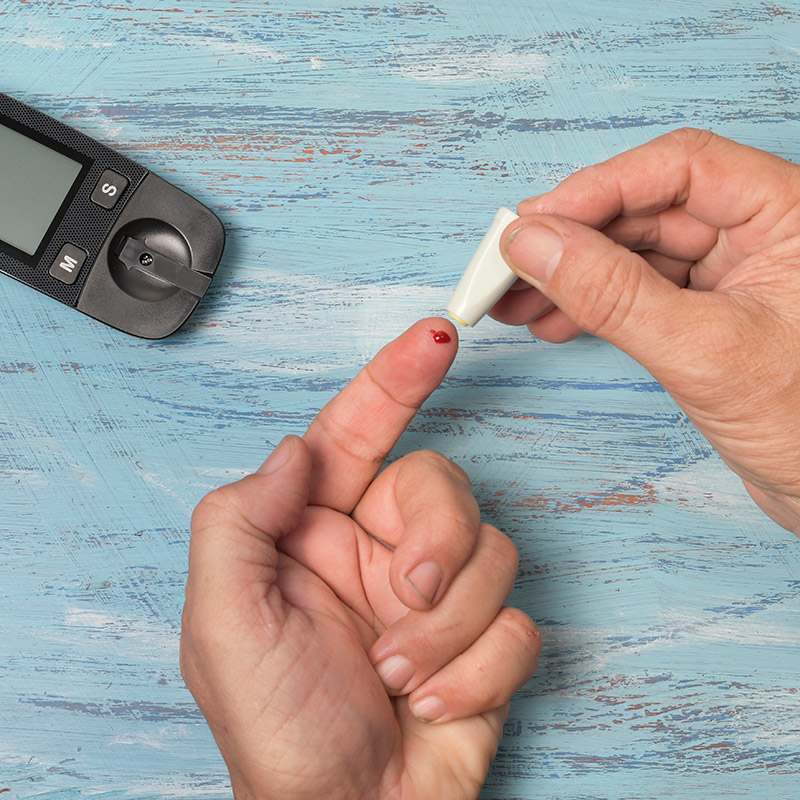
Metabolic Syndrome is a cluster of conditions, which, when present at the same time, lead to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease or diabetes.
These risk factors are:
- High levels of LDL cholesterol and low levels of HDL cholesterol
- High levels of blood triglycerides
- Insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels
- Arterial hypertension (>140/90 mmHg)
- Obesity (BMI>30) and large waist circumference (>94 cm for men and> 80 cm for women)
Metabolic Syndrome is diagnosed when 3 or more of these risk factors are present.